Sci-tech Innovation Powers Spring Plowing

By WANG Xiaoxia
China's first document for the year, the "No. 1 central document" issued in February, emphasizes the importance of developing new quality productive forces in agriculture in light of local conditions. The development of smart agriculture will be supported and the application scenarios of technologies such as AI, big data, and low-altitude systems will be expanded.
With the arrival of spring and farmers getting busy across the country, sci-tech innovation is boosting agricultural production, not only bringing tangible benefits to farmers, but also injecting new impetus into rural revitalization. Science and Technology Daily looks at the changed farming scenario across provinces.
Intelligent machines
Drone fertilization, remote controlled drip irrigation, machine seedling transplantation... modern technologies and intelligent tools are transforming and upgrading traditional farming, facilitating farmers' work and reducing costs.
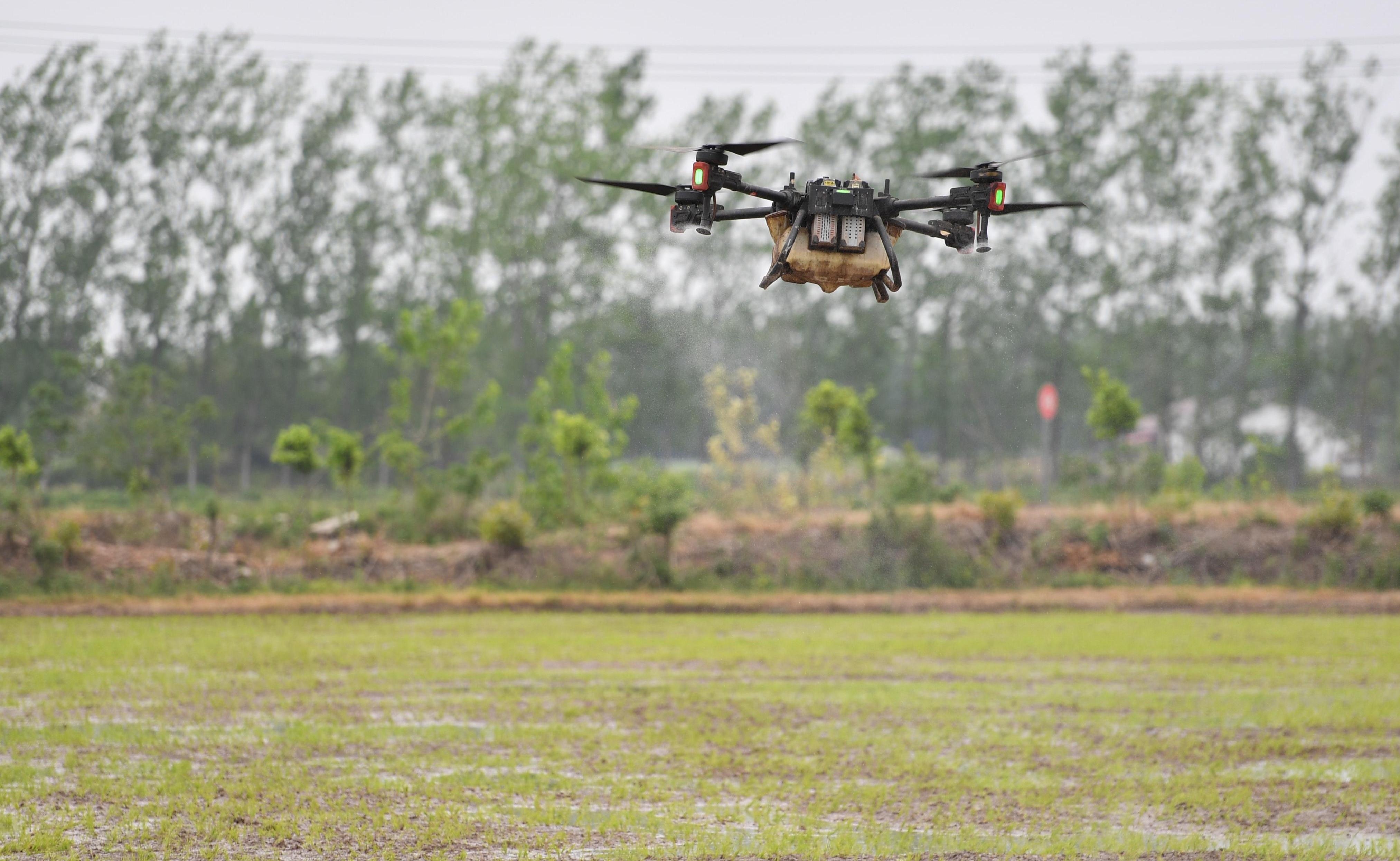
In an unmanned agricultural cooperative in Gaochun District in Nanjing, Jiangsu province in east China, a DJI T100 plant protection drone with a load of 150 kg of herbicide flies over a wheat field and sprays herbicide evenly.
The intelligent system installed on the machine can automatically scan the field and spray herbicide accurately, said Wei Qing, the head of the cooperative.
A smart platform records the plant varieties, agricultural machinery operations and other data in detail. All intelligent equipment can be controlled online, and the cost to fertilize fields is reduced by about 120 RMB per mu (one mu equals 666.67 square meters) compared with the original manual fertilization method.
According to the Nanjing Municipal Bureau of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, the city has more than 1,000 agricultural plant protection drones, which can be used for fertilization, weeding, field patrol and other plant protection work.
Seed selection technology
In Changsha in central China, researchers at the germplasm resource bank of the Yuelu Mountain Laboratory are putting the seeds into an instrument that is a novel seed scanner. On the screen of the nearby computer, the scan result — the spectral curve of the seed — appears clearly.
The scanner, called the "rice seed vigor detection sorter," is used to do CT scans of the seeds to judge whether they are good or not, explained Yu Yinghong, president of the Hunan Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
In the past, farmers had to wait for the seeds to germinate before they could see whether the seeds were dead or alive, good or bad, which was an inefficient way, Yu said. Therefore, the Hunan Academy of Agricultural Sciences and the Chinese Academy of Sciences jointly developed the seed scanner, the first of its kind in the world.
Good seed quality and high germination rate are crucial for the output. The right varieties have to be chosen according to the conditions of different regions, farmers' needs and their habits, said Bai Lianyang, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering.
Smart management
As the temperature rises, more than 43 million mu of wheat in Anhui province have entered a critical period: They are greening up, with green shots appearing and the first swollen nodes emerging above the soil surface, a stage called jointing. The local government has made full use of the smart field management system to enhance management accuracy and improve operation efficiency.
Chang Xingduo, a farmer in Taihe, a county in Fuyang, Anhui province in the east, receives an early warning on his mobile phone. It's from an app, "Smart Agriculture Cloud," telling him that wheat spiders and aphids have been detected in his field and need to be controlled quickly.
Chang quickly sends out his plant protection drones and self-propelled sprayers to pest-control his 3,200-mu field.
Since 2021, Taihe has been promoting intelligent field management of wheat, and has built nearly 20 field monitoring points. Now its smart field management system covers more than 1.52 million mu of wheat fields.
With this system, grain growers can monitor the growth of wheat in real time on their mobile phones, and the agricultural department can also provide technical guidance to farmers through it.